With the launch of the 2023 OT Cybersecurity Year in Review, we stand at the crossroads of unprecedented challenges and unparalleled opportunities. The past year was marked by geopolitical strife that heavily influenced the operational technology (OT) threat landscape, affecting industrial sectors worldwide. Ransomware attacks not only increased in frequency but also in their impact on businesses, while the accumulation of vulnerabilities in industrial systems highlighted critical areas of concern. Although there have been strides towards improvement in certain sectors, punctuated by notable successes in OT cybersecurity, the journey is far from complete. The urgency to fortify OT against the rising tide of cyber threats has never been more critical. The path forward is clear, and the time is now.
Our 7th annual report on the state of OT cybersecurity covers extensive ground, capturing a year’s worth of threats, weaknesses, and victories. It combines research from across Dragos: our world-class cyber threat intelligence, first-hand stories, and statistics from the trenches of OT cyber defense, first-party data from Neighborhood Keeper, along with analysis of the totality of vulnerabilities that impacted industrial systems. It’s not just an account of what’s been, but also a compass for what lies ahead.
These exclusive insights and proactive recommendations will steer OT asset owners and defenders through the coming year. Find out what went right in the world of OT cybersecurity, what went wrong, and what could have gone worse, were it not for a unified response from across the OT community. Read on for some highlights from the 2023 OT Cybersecurity Year in Review report.
Explore 2023 Year in Review Data
Discover highlights and exclusive insights from our 2023 OT Cybersecurity Year in Review.
Explore the DataThreat Groups Targeting OT
Dragos Intelligence researches and tracks the activities of threat groups targeting industrial organizations and critical industrial control systems (ICS). Currently there are 21 threat groups currently being monitored by Dragos adversary hunters.

Dragos Intelligence identified three new threat groups in 2023. All three groups possess capabilities that target and exploit public-facing infrastructure used or owned by victim organizations. None of the three threat groups have been observed using any ICS-specific capabilities; however, their persistent interest in industrial organizations and access to sensitive OT data is a cause for concern.
 | VOLTZITE, which overlaps with Volt Typhoon (Microsoft), was first observed performing reconnaissance and enumeration of multiple electric companies based in the United States. They have been observed conducting reconnaissance and enumeration of multiple US-based electric companies, and since then has been observed targeting electric power transmission and distribution, emergency services, telecommunications, defense industrial bases, and satellite services. |
 | GANANITE targets critical infrastructure and government entities in the Commonwealth of Independent States and Central Asian nations. GANANITE focuses on espionage and data theft, with the possibility of handing off initial access to other threat groups. This group is focused on its target sets and employs many known tools and techniques to infiltrate its victims. |
 | LAURIONITE was first discovered actively targeting and exploiting Oracle E-Business Suite iSupplier web services and assets across several industries, including aviation, automotive, manufacturing, and government. Oracle E-Business Suite is one of the most widely used enterprise solutions for integrated business processes, including at numerous industrial organizations. |
Secure Remote Access is critical to securing OT environments against these threats. A key method, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a rare case of a classic IT control that can be appropriately applied. Focused monitoring of connections in and out of the OT network is also essential.
Conflict-Driven OT Cyber Threats
Wars are fought on many fronts, where opponents will exploit any weakness, and no element is beyond the scope of weaponization. This timeless principle now unequivocally encompasses OT in critical infrastructure, marking it as a critical arena in contemporary conflicts. This is demonstrated by several advanced threat groups active in 2023 including ELECTRUM, KAMACITE, and VOLTZITE, a new threat group identified this past year, all of them driven by geopolitical agendas. To those same ends, unsophisticated hacktivists also set their sights on industrial organizations, finally breaking through when the self-styled CyberAv3ngers hacktivist group successfully executed disruptive attacks on OT and impacted critical utilities in the United States and Europe.
Using cyber threat intelligence to maintain situational awareness of geopolitical conflicts that intersect with operational technology cybersecurity is paramount to understanding the motivations and targeting objectives of several advanced OT adversaries, as well as those of hacktivists with fewer resources but comparable determination.
Living Off the Land (LOTL) Techniques
Several OT cyber adversaries employ living off the land (LOTL) techniques as means to achieve their objectives. Using native tools already present in industrial networks, and the exploitation of valid or default credentials, looks normal. They’re able to stay hidden longer. The VOLTZITE threat group tracked by Dragos Intelligence makes heavy use of LOTL techniques. This strategy, paired with slow and steady reconnaissance, enables VOLTZITE to stay persistent in environments for considerable periods of time, which in turn impairs detection and response efforts. Dragos Professional Services utilized these same LOTL techniques effectively in 63 percent of its penetration testing engagements across both Stage 1 and Stage 2 of the ICS Cyber Kill Chain.
Maintaining an inventory of assets and actively monitoring traffic for potential threats is a good start to improved visibility and monitoring. LOTL techniques require more than just your basic anomaly detections. Behavioral detections using the latest adversary tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) will usually be necessary.
Industrial Risk of Ransomware
Fifty ransomware groups were responsible for 905 reported ransomware incidents impacting industrial organizations this past year. This represents a 49.5 percent increase from 2022.
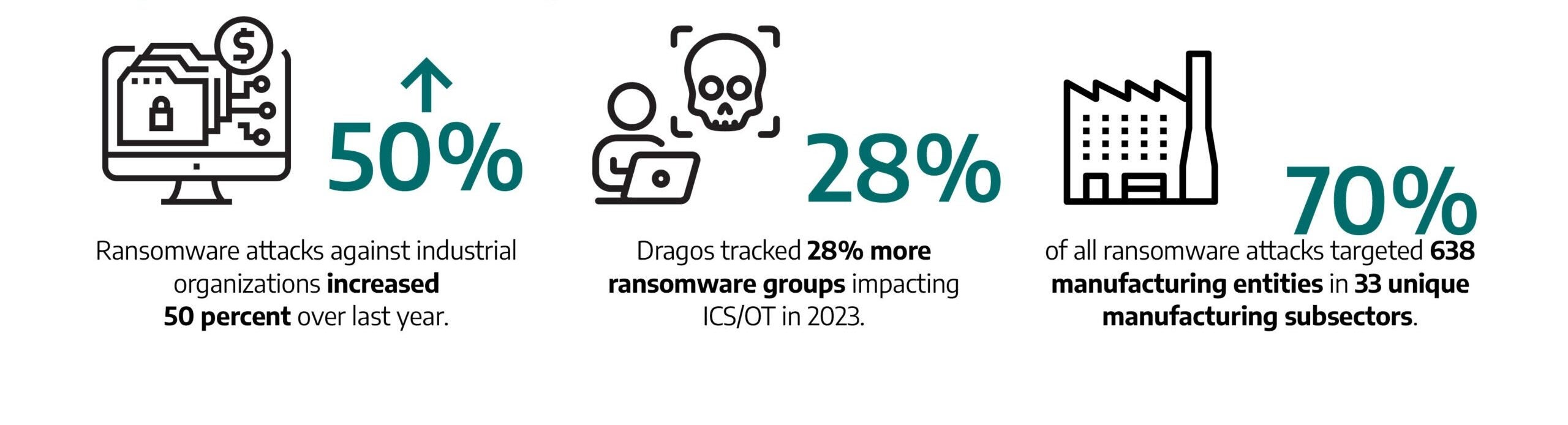
Industrial organizations have much to lose because operational disruptions can carry significant financial and reputational costs. Further, there can be numerous cascading impacts on downstream businesses and outputs. The most common sector impacted in 2023 was manufacturing, with 70 percent of ransomware incidents.
Ransomware attacks that spread into OT can disrupt business operations, and it can take time to get systems up and running again. This requires a gates and fences approach. A defensible architecture often starts with hardening the environments, such as removing extraneous OT network access points, firewall rules for external networks, and network segmentation.
The State of OT Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities stacked up faster than unread emails in an inbox this past year. Dragos Intelligence independently assessed, corrected, and augmented 2010 vulnerabilities impacting industrial systems in 2023.

In the Dragos Platform, that analysis is used to categorize OT vulnerabilities by NOW, NEXT, and NEVER, and last year, only 3 percent of vulnerabilities needed to be addressed NOW, meaning the remainder can be addressed in other ways such as monitoring and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
While patching an IT system like a worker’s laptop is relatively easy, shutting down a plant is a costly and time-consuming. Most of the time, it’s not even necessary. Knowing what to do and how urgently that is needed are the core principles behind an effective risk-based vulnerability management program.
Incident Response to OT Threats
This shift was not perceived equally across industry verticals, but nearly all verticals increased focus on tabletop exercises. The most significant increase was seen in the electric sector, where the tabletop exercises’ share of reports in that sector increased 104 percent year over year. Throughout the industrial space, teams are shifting focus toward tabletop exercises.
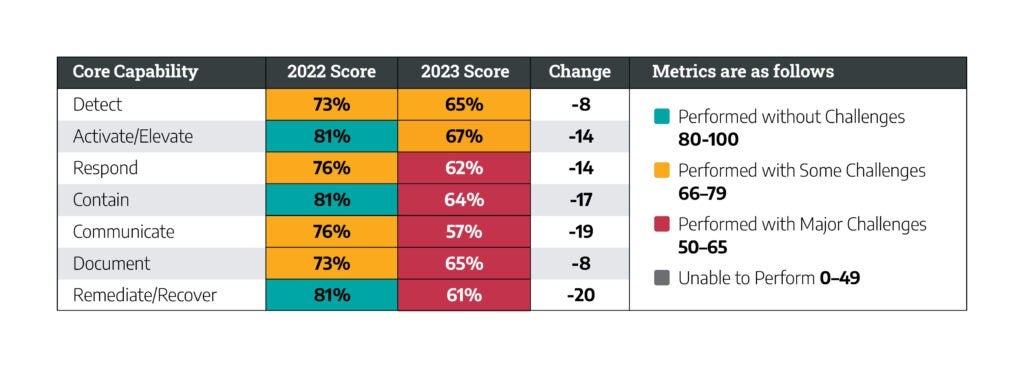
Be proactive about having an OT incident response plan (IRP) that is distinct from IT’s. OT involves different devices, communication protocols, adversary behaviors, and vulnerability management practices. Cyber attacks can result in physical impacts and investigations require a different set of tools. Create a dedicated plan that includes the right points of contact and next steps for specific scenarios at specific locations.
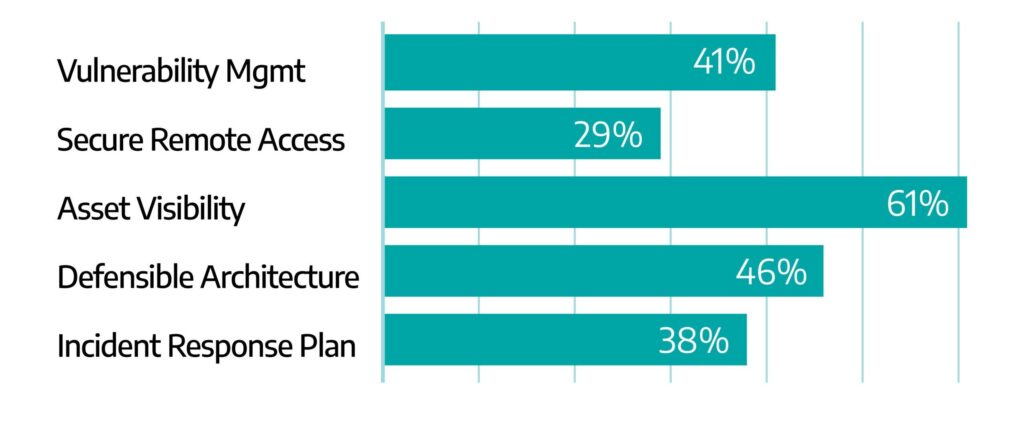
Developing resiliency is a focal aspect of the SANS 5 Critical Controls for World-Class OT Cybersecurity. Of Dragos Professional Services engagements in 2023, 94 percent had a finding relating to one of these controls, and improving OT network visibility tops the list appearing in more than half of our reports.
Get Your Copy of the 2023 Year in Review
For all this and much, much more, read the 2023 OT Cybersecurity Year in Review. Start your journey towards enhanced OT threat preparedness with exclusive data, research, and insights from Dragos.
Ready to put your insights into action?
Take the next steps and contact our team today.

